 |
Nepal SOCIAL LIFE |
|
 |
Nepal Information |
|
|
 |
|
Dalits -
lowest Hindu caste
|
 |
| Who
are the Dalits? |
 |
Since
Dalits perform menial tasks, traditional societies consider them "unclean."
Higher castes are thus required to avoid close contact with Dalits, leading
to a generations old segregation of society. The Dalit caste has further
been divided into different groupings in accordance with the type of work
the groups are limited to. For example, communities engaged in tailoring,
or playing musical instruments, or communities involved in washing clothes,
or in making clay pots, or working with metal will be given different family
names in accordance to the type of work they do. Dalits are often referred
to as the occupational or artisan caste.
 |
 |
 |
The
ongoing discrimination of Dalits in Nepali society proves a major obstacle
to the overall human development in the country. Deep rooted beliefs about
the impurity of Dalits have been difficult to transform. Recurring incidents
of discrimination at public water taps, restaurants, milk co-operatives
(milk supplied by Dalits is refused). and temples are daily occurrences.
For example in one incident, a three-year-old girl from Sindhupalchowk
District was beaten to death by a high-caste Brahmin woman when the girl
touched a high-caste water-well. In another incident in Silgadhi Municipality,
in Doti District a group of Dalit women tried to enter the famous Saileshwori
Temple. They were refused entry although Dalits are also Hindus, they are
excluded from worship at temples. Such incidents continue to be common
for many Dalits.
Due
to their poor economic and educational status, Nepalese dalits have been
exploited since ages. Especially after the restoration of democracy in
1990 they have fallen victim to rice-Christianity and Maoist movement.
Since early childhood, from playgroup to school and college they were ostracised.
Even the teachers discriminated them. Even in the most developed cities
like Katmandu Dalits have to hide their identities to get a rented appartment.
Caste
discrimination in public places is theoretically illegal in Nepal since
1963. Nepal has signed all international treaties and conventions against
racial discriminations. The democratic Constitution of Nepal 1990 clearly
states the Right to Equality and Non-Discrimination. Despite these laws
and rules, discrimination is still practiced in Nepalese society.
The
Hindu religion has categorized Shudras (Dalit or untouchables) as
the serving class and in some scriptures they have been denied even the
human status. From centuries, they have been barred from sharing public
amenities; water taps, wells, schools, temples and tea stalls with the
uppercaste. The Manusmriti is so harsh against Shudras that it bars them
from acquiring property and treats them as pariahs. In ancient times, their
life was worse than that of animals. In the 14th century, King Jayasthiti
Malla, a King of Kathmandu formalised this system. He caterogised castes
based on their work; touchables and untouchables. And in 1853, Prime Minister
Janga Bahadur Rana further reinforced the discrimination by bringing a
Civil Code.
The
number of Dalits in the Maoist movement is high. According to estimates
of a US about 30 percent of the People's Liberation Army are dalits. According
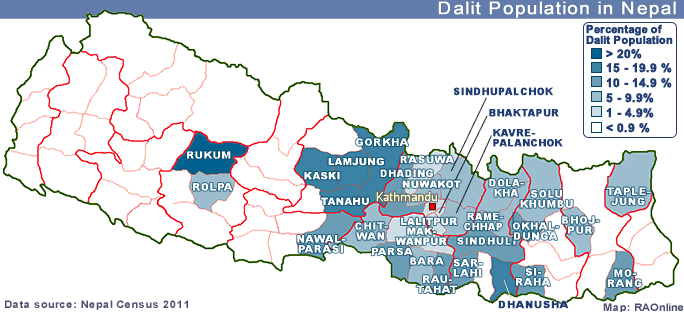
to the National Census 2001, Dalit population hovers around 4.5 million,
which is over 20 per cent of the population of Nepal.
top
| Facts
about Dalit |
 |
 |
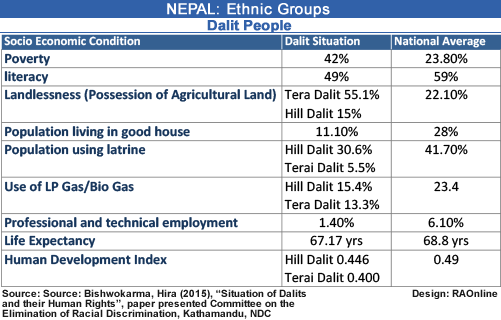
Dalits
make up 20% of the total population |
 |
80%
of the Dalit population lives below the poverty line |
 |
Per
capita income= US $ 39.6 |
 |
Literacy
rate: 10% (19.64%, SCF source) |
 |
Female
Literacy rate: 3.2% (9.65%, SCF source) |
 |
Share
of Dalits in cultivable land:1% |
 |
70%
of Dalits are malnourished |
 |
Life
expectancy: 42 |
Source:
National Dalit Preparatory Committee Nepal for WCAR |
 |
| more information |
 |
top
|
Links
|
 |
 |
 |
Externe
Links |
|









